Looking for the list of the Most Important Muscles for Baseball? This is the article for you!
Baseball is a sport that demands talent, strategy, and physical fitness. To perform well on the field and at bat, players must have powerful muscles. We will look at the most vital forces for baseball players, their functions, and how to improve their performance in this complete guide. Understanding these critical muscles will surely improve your game and offer you a competitive edge, whether you are a seasoned player or just starting out.
25 Most Important Muscles for Baseball
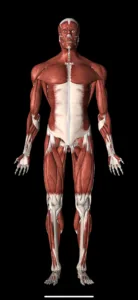 Let's look at the essential muscles that play a role in baseball and why they are important for optimal performance:
Let's look at the essential muscles that play a role in baseball and why they are important for optimal performance:
- Muscles of the Core
Any baseball player's foundation is built on a strong core. It consists of the abdominal, obliques, and lower back muscles. During hitting, throwing, and fielding, the core offers stability, balance, and power. Core-specific workouts like planks and medicine ball twists will help strengthen these muscles, resulting in better performance on the field. - Muscles of the Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff is a collection of tendons and muscles that surround the shoulder joint. During throwing, these muscles are critical for arm stability and control. Baseball players' shoulders are frequently subjected to repetitive and high-velocity maneuvers, making the rotator cuff muscles vulnerable to injury. Regular rotator cuff workouts, including external and internal rotations, prevent injuries and maintain strength. - Hamstrings and Quadriceps
Baseball requires strong quadriceps and hamstrings for running, jumping, and explosive actions. Players with strong quadriceps muscles can produce power while batting and sprinting the bases. On the other side, strong hamstrings aid in speed and agility. Squats, lunges, and deadlifts should be included in your workout regimen to target these muscle groups. - Gluteus Maximus Muscles
Baseball relies heavily on the gluteus muscles, notably the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus. They are in charge of hip extension, which is necessary for running, jumping, and staying balanced during lateral motions. Glute muscle strengthening workouts include hip thrusts, leg presses, and lateral band walks. - Flexors and extensors of the forearm
A successful baseball player must have good bat control and grip strength. Wrist movements and grip strength are controlled by the forearm flexors and extensors. These muscles can be strengthened to improve bat control and prevent wrist injuries. Exercises such as wrist curls and reverse curls can efficiently target these muscles. - Calves
Running, jumping, and fast movements on the field all use the calf muscles. Players with powerful calves have explosive speed, which can be a game changer in important situations. Calf raises and plyometric workouts should be included in your training routine to improve these muscles.  Latissimus Dorsi muscle
Latissimus Dorsi muscle
The latissimus dorsi, or lats, are big muscles in the back that are responsible for shoulder extension and stability. During throwing and swinging motions, these muscles are activated. To improve your throwing power and accuracy, strengthen your lats with pull-ups, rows, and lat pulldowns.- Adductors and Abductors
Abductors and adductors are required for lateral movement and hip stability. Baseball players routinely shift laterally, particularly in the outfield. Maintaining the strength of these muscles can improve agility and lessen the incidence of hip injury. These muscular groups can be targeted with exercises such as lateral lunges and standing leg raises. - Pectoral Muscles
Baseball activities involving the pectoral muscles, or pecs, include throwing, swinging, and diving catches. Strong pecs help with upper body strength and power. Push-ups, bench presses, and chest flies can all aid in the development of these muscles. - Triceps
Throwing and pushing motions engage the triceps. Triceps strength helps increase throwing velocity and control. Tricep dips, skull crushers, and overhead extensions are all good exercises for these muscles. - Biceps
While the triceps are important for pitching, the biceps are important for batting. Biceps that are strong allow players to produce power during their swing. Bicep curls and hammer curls are great exercises for these muscles. - Hip Flexors
Baseball actions involving the hip flexors include running, fielding, and throwing. Maintaining flexibility and strength in them can increase range of motion and lessen the likelihood of hip injury. Include leg lifts and hip flexor stretches in your workout program. - Transverse Abdominis
The transverse abdominis is a deep abdominal muscle that supports and stabilizes the spine. A strong transverse abdominis can aid in the prevention of lower back ailments. Engage this muscle by performing exercises such as plank variants and bird-dog positions. - Serratus Anterior
The serratus anterior, popularly known as the "boxer's muscle," is found on the chest's sidewalls. It aids with scapula stabilization and enables for smooth shoulder movement during throwing and swinging. Exercises such as push-ups with a plus and scapular wall slides can help to strengthen this muscle. - Obliques
Baseball rotational actions, such as swinging and throwing, rely on the obliques. Oblique strength improves core stability and power. Include Russian twists and side plank rotations in your workout program. - Thoracic Transversus
The transversus thoracic is a small muscle on the interior of the chest. It aids in breathing and ribcage stabilization during powerful exhalations. Proper breathing is vital for baseball endurance and performance. Deep breathing exercises should be practiced to adequately engage this muscle.  Gastrocnemius muscle
Gastrocnemius muscle
The gastrocnemius, also known as the calf muscle, is essential for explosive actions such as running and jumping. Calves that are strong and flexible can improve running speed and agility. Calf stretches and calf raises can help to keep these muscles in shape.- Teres Major
The teres major is a shoulder muscle that works with the latissimus dorsi to move the arm. It aids in throwing and swinging actions. Exercises such as rows and lat pulldowns can help to strengthen this muscle. - Subscapularis
The subscapularis is a rotator cuff muscle found on the front of the shoulder blade. It is required for shoulder internal rotation during throwing. Internal rotation workouts with tension bands might help you target this muscle. - Infraspinatus
Another rotator cuff muscle important for external shoulder rotation is the infraspinatus. When throwing, strong infraspinatus muscles aid in shoulder stability. To target this muscle, use external rotation workouts with resistance bands. - Supraspinatus
The supraspinatus muscle is the third rotator cuff muscle, and it helps with shoulder abduction. It is activated during the throwing motion. Exercises such as lateral lifts and shoulder presses can help to strengthen this muscle. - Rhomboids
The rhomboids, which are positioned between the shoulder blades, help with scapular retraction and stability. Rhomboids that are strong can assist prevent shoulder injuries and improve throwing mechanics. Exercises like bent-over rows and wall slides can help to strengthen them. - Erector Spinae
The erector spinae muscles, which run along the spine, are essential for maintaining an upright posture and stability during bending movements. Exercises such as deadlifts and back extensions can help to strengthen these muscles. - Gluteus Medialis
The gluteus medius is in charge of hip abduction and assists with balance during running and lateral movements. Exercises that target this muscle include lateral band walks and side-lying leg raises. - Superficial Digitorum Flexor
The flexor digitorum superficialis is a forearm muscle that allows you to bend your fingers. A strong grip is essential for baseball players, and this muscle helps with grip strength. Exercises such as gripping exercises and wrist curls might help to strengthen it.
Optimal Muscle Development for Peak Performance
Pitchers' TopVelocity 3X Velocity Program
 The TopVelocity 3X Velocity Program is a complete training routine designed exclusively to increase pitching velocity and overall performance on the mound. This program focuses on the most vital baseball muscles, allowing pitchers to achieve optimum performance and execute forceful throws.
The TopVelocity 3X Velocity Program is a complete training routine designed exclusively to increase pitching velocity and overall performance on the mound. This program focuses on the most vital baseball muscles, allowing pitchers to achieve optimum performance and execute forceful throws.
- Strong Leg Power
Developing explosive leg power is a major component of the TopVelocity 3X Velocity Program. Pitchers' lower bodies provide a major amount of their throwing velocity. A sequence of plyometric exercises, such as box jumps and forceful squats, are included in the program to develop the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glute muscles. Pitchers can push off the mound with more force if their leg power is optimized, resulting in faster deliveries. - Stability and Strength of the Core
Pitching demands outstanding core stability to efficiently transfer energy from the lower to the upper body. To strengthen the abdominal muscles and obliques, the 3X Velocity Program involves a range of core-specific workouts such as medicine ball twists and cable wood chops. Pitchers with a strong core may maintain optimal body alignment during the delivery, resulting in more precise and forceful tosses.  Arm and Shoulder Conditioning
Arm and Shoulder Conditioning
The program includes targeted shoulder and arm fitness exercises to help avoid shoulder problems and improve arm strength. These workouts work the rotator cuff muscles, including the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis, which are important for shoulder stability during the pitching motion. The program also includes arm care exercises and stretching routines to keep your shoulders healthy and flexible.- Dynamic Flexibility and Mobility
The TopVelocity 3X Velocity Program emphasizes dynamic mobility and flexibility exercises to increase the hip, shoulder, and thoracic spine range of motion. Pitchers with increased mobility can achieve optimal pitching mechanics while avoiding undue stress on their joints. It also allows them to generate more arm speed, which results in higher pitch velocity. - Drills for Throwing
To increase arm strength and endurance, the program involves a variety of throwing-specific routines, such as long toss and weighted ball exercises. These workouts imitate game-like scenarios and help pitchers improve the muscle memory needed to continuously repeat efficient mechanics.
The Position Players 2X Velocity Program
 Position players, such as infielders, outfielders, and catchers, require a distinct set of skills on the field than pitchers. The 2X Velocity Program is designed specifically for position players, assisting them in optimizing muscle development for top performance in their roles.
Position players, such as infielders, outfielders, and catchers, require a distinct set of skills on the field than pitchers. The 2X Velocity Program is designed specifically for position players, assisting them in optimizing muscle development for top performance in their roles.
- Rapid Agility and Quickness
To excel in their defensive positions and on the bases, position players must have explosive agility and quickness. To improve footwork and response time, the 2X Velocity Program contains agility ladder drills, cone drills, and lateral movements. Strong gluteus muscles, as well as hip abductors and adductors, are required for performing quick actions such as diving catches or swiping bases. - Bat Power and Speed
Bat speed and power are crucial for position players to succeed at the plate. To improve bat control and swing power, the program includes exercises that target the forearm flexors and extensors, as well as the core muscles. Strengthening the biceps and triceps also helps to generate more force throughout the swing, which results in harder-hitting balls.  Quick-Response Throws
Quick-Response Throws
Position players, particularly infielders, must make quick and accurate throws in order to record outs. Drills to develop arm strength and throwing mechanics are included in the 2X Velocity Program. The ability to make strong and precise throws across the diamond is improved by targeting the rhomboids, serratus anterior, and latissimus dorsi muscles.- Stamina and endurance
Position players are frequently involved in lengthy and physically difficult games. Endurance training is used in the program to increase stamina and reduce exhaustion during extended play. Cardiovascular activities, as well as specific muscle training, ensure that position players can perform at their best throughout the game. - Flexibility and Injury Avoidance
Finally, position players, like pitchers, benefit from a concentration on flexibility and injury prevention. Stretching and exercises that target the hip flexors, hamstrings, and calf muscles on a regular basis help to maintain flexibility and lessen the risk of injury during dynamic movements on the field.
The TopVelocity 3X Velocity Program for pitchers and the 2X Velocity Program for position players are comprehensive baseball training programs designed to optimize muscle development and optimum performance. These programs address pitchers' and position players' individual demands, assisting them in strengthening the most crucial muscles for their respective responsibilities on the field. Whether you want to improve your pitching velocity or your position-player skills, these programs offer a disciplined and practical method to take your game to the next level.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions): Most Important Muscles for Baseball
Q: How can I avoid shoulder problems when playing baseball?
A: It is critical to warm up adequately before engaging in any physical activity to avoid shoulder injury. Exercises that strengthen the rotator cuff muscles, such as external and internal rotations, should be included. Maintain appropriate throwing mechanics as well as avoid overuse of the shoulder.
Q: Can baseball players benefit from weightlifting exercises?
A: Yes, baseball players can benefit greatly from weightlifting training. Strength training can help you enhance your overall performance, power, and endurance on the field. Exercises that target the primary muscles outlined in this guide should be prioritized.
Q: For baseball, should I prioritize cardio or strength training?
A: Baseball players must engage in both aerobic and weight training. Cardiovascular exercise promotes endurance and speed, but strength training improves power and overall performance. The finest benefits will come from balancing both types of exercises in your training plan.
Q: What can I do to improve my bat speed?
A: Work on strengthening your core, hips, and forearms to increase bat speed. Additionally, use good hitting skills and use resistance training to improve your swing's explosiveness.
Q: What should I do if I have muscular discomfort after working out?
A: Although muscle pain after exercise is natural, severe discomfort may indicate overtraining. Allow your muscles to rest and heal between strenuous workouts. Consider including stretching and foam rolling into your healing routine.
Q: Can I still play baseball if my muscles are weak?
A: Baseball demands both talent and physical fitness. While weak muscles can hinder your performance, they do not preclude you from playing. To gradually enhance your game, work on strengthening the main muscles indicated in this tutorial.
To summarize, baseball players must have well-developed and strong muscles. Each muscle group contributes to different facets of the game, including as hitting, throwing, and fielding. You may improve your performance and flourish on the field by recognizing the most vital muscles for baseball and adding focused exercises to your training regimen. Remember to keep good form and, if necessary, get advice from a competent trainer.
So, start developing those muscles and prepare to take your baseball skills to the next level!


 Gastrocnemius muscle
Gastrocnemius muscle Arm and Shoulder Conditioning
Arm and Shoulder Conditioning
 Quick-Response Throws
Quick-Response Throws
