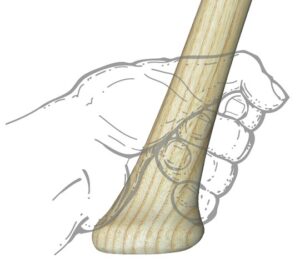
 In baseball, the Hitting Grip and Hand Position is not just a matter of personal comfort or style—it's a critical factor that can greatly affect their performance at the plate and their overall risk of injury. One of the more serious injuries associated with batting is the hook of hamate fracture. This type of injury occurs in the small, hook-shaped bone in the wrist known as the hamate, which is particularly susceptible to stress in sports that require tight gripping of equipment, such as baseball, golf, and tennis.
In baseball, the Hitting Grip and Hand Position is not just a matter of personal comfort or style—it's a critical factor that can greatly affect their performance at the plate and their overall risk of injury. One of the more serious injuries associated with batting is the hook of hamate fracture. This type of injury occurs in the small, hook-shaped bone in the wrist known as the hamate, which is particularly susceptible to stress in sports that require tight gripping of equipment, such as baseball, golf, and tennis.
Understanding the relationship between hand grip, bat swing, and the resultant pressure on the hamate is crucial for athletes looking to optimize performance while minimizing injury risks. To address this, the study explored in this article examines how various batting grips and swing techniques influence the distribution and intensity of pressure on the hamate bone. The research aims to identify specific grips and swing types that might increase the likelihood of a hamate fracture, thereby providing valuable insights for players and coaches to make informed decisions about technique and training practices. This investigation is especially pertinent given that changes in grip and swing mechanics could potentially offer straightforward modifications to significantly reduce the risk of enduring such debilitating injuries.
Case Study Overview: Hitting Grip and Hand Position
Flynn, L. S., Richard, G. J., Vincent, H. K., Bruner, M., Chen, C., Matthias, R. C., ... & Farmer, K. W. (2021). Swing type and batting grip affect peak pressures on the hook of hamate in collegiate baseball players. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine, 9(12), 23259671211060807.
The primary objective of this research was to delve into how different batting grips and swing methods influence the pressures exerted on the hook of the hamate. This small bone, situated in the wrist, plays a pivotal role in the mechanics of batting but is also vulnerable to fractures, particularly in sports that require the use of a bat. By analyzing the distribution of pressure across this bone during various batting scenarios, the study aimed to uncover which techniques may heighten the risk of injury.
This comprehensive analysis involved measuring the physical forces acting on the hamate during a range of batting actions to determine potential stress points that could lead to fractures. Such fractures can sideline players, causing significant disruptions in their careers and performance. Therefore, gaining a deeper understanding of these pressures is essential for developing strategies to prevent such injuries. The research not only looks at the immediate impact of different grips and swings but also examines long-term implications for player health and career longevity. This insight is crucial for coaches, trainers, and players themselves who seek to optimize performance while ensuring safety in the sport.
Research Significance: Hitting Grip and Hand Position
The significance of this research extends beyond academic interest, addressing a critical concern in the world of sports medicine and athletic training. Hamate fractures are particularly troublesome due to their potential to drastically interrupt an athlete's career—sometimes to the point of a premature end—owing to the prolonged recovery times and the possibility of recurring issues if not rehabilitated properly. Given the severity and the impact of such injuries, the study's findings are instrumental in offering empirical data that can lead to better preventative strategies.
By dissecting the mechanics of various batting grips and swing styles, the research elucidates how different techniques exert distinct pressures on the hamate bone. This knowledge is invaluable as it helps coaches and athletes understand which specific aspects of their batting technique may need adjustment to reduce the risk of injury. As a result, training programs can be tailored more effectively, incorporating these insights to refine techniques, enhance safety, and optimize performance.
Moreover, the study serves as a foundational resource for further investigations and developments in sports equipment design, possibly leading to innovations in bat ergonomics to better accommodate safer grip positions. Ultimately, the practical applications of this research equip sports professionals with the tools to make informed decisions that prioritize athlete health, potentially extending playing careers and improving the overall quality of the sport.
Participants and Methodology: Hitting Grip and Hand Position
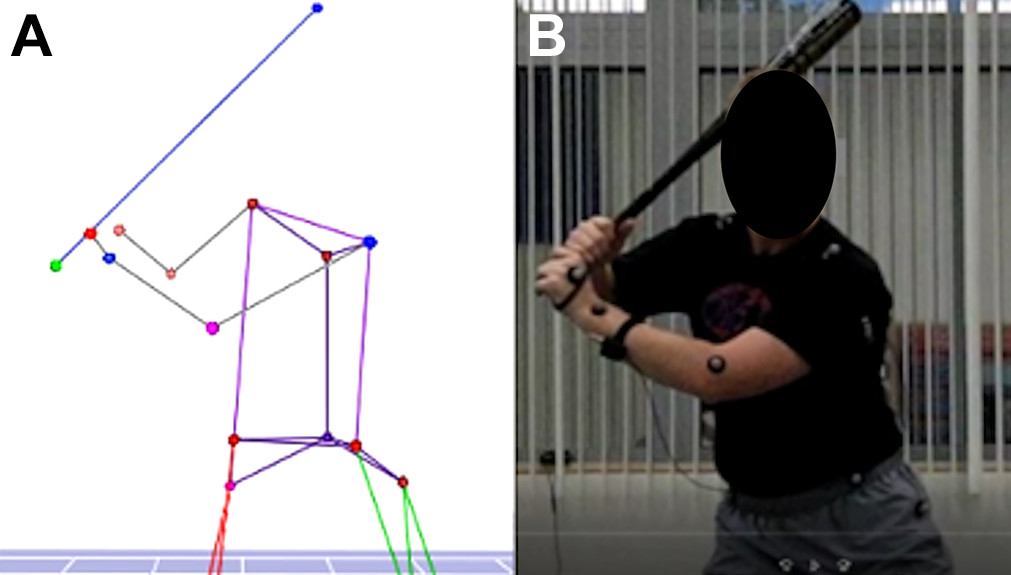
In this study, a focused group of fourteen male collegiate baseball players from the University of Florida was selected to participate in a quasi-randomized pilot study designed to explore the biomechanics of batting. This group was chosen to provide a homogeneous sample representative of active athletes who are regularly exposed to the rigors of competitive baseball, thereby ensuring the relevance and applicability of the study results to similar athletic populations.
Participants were carefully screened to exclude any individuals who had sustained recent injuries or who might not fully comprehend the study procedures, ensuring that all data collected would be as reliable and consistent as possible. This selection criteria was vital to maintaining the integrity of the study, as recent injuries could alter natural swing mechanics or grip strength, thereby skewing the results.
During the study, researchers employed sophisticated measurement techniques to accurately assess the grip pressures exerted by the players. Additionally, detailed analyses of bat swing mechanics were conducted under a variety of controlled conditions. These conditions were designed to mimic real-game scenarios as closely as possible, thereby providing practical insights into how different batting techniques affect the pressures on the hamate bone.
By employing a methodical approach to both participant selection and data collection, this study aimed to yield high-quality, actionable insights that could potentially transform coaching practices and player training routines, ultimately contributing to reduced injury rates and improved player performance in baseball.
Bat Grip Variations Examined: Hitting Grip and Hand Position
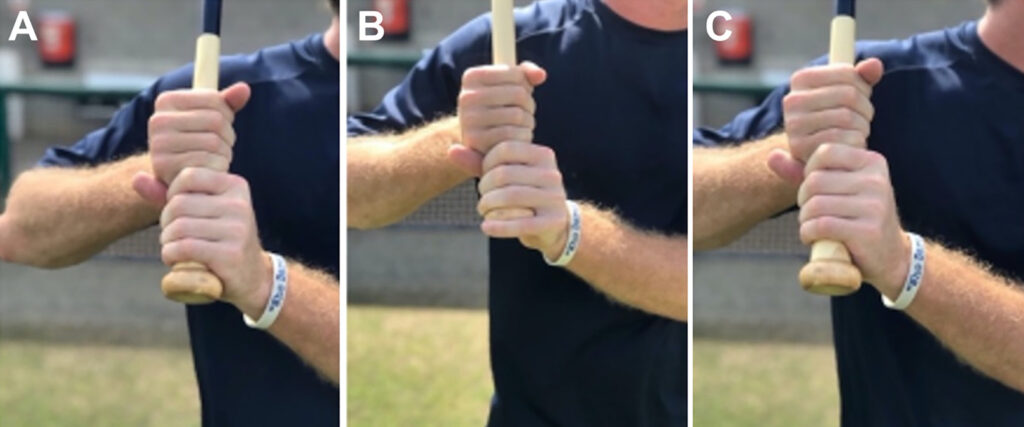
In the study, researchers carefully analyzed the impact of three distinct bat grip conditions on the pressure exerted on the hamate bone. These grip conditions were chosen to reflect common variations in how players typically handle a bat, providing a broad spectrum of real-world batting styles.
- All On (AO): In this grip configuration, all fingers of the hand were above the bat knob, which is a conventional grip that many players use. This setup was tested to evaluate how a conventional grip distributes pressure across the hamate bone during swings.
- One Off (OF): For this condition, the smallest finger, or pinky, was positioned off the bat knob. This grip variation is less traditional but is used by some players who feel it provides better control or comfort. This setup was examined to determine if removing one finger from direct contact with the knob alters the stress profile on the hamate.
- Choked Up (CU): In this grip, the hands were about 3.75 cm above the knob, which is a tactic that players frequently use to reduce the bat's swing radius for better bat control. This grip was included to assess how such a positional adjustment influences the pressure exerted on the hamate during batting.
Each of these grip variations was further tested with two types of swings: full swings and check swings. A full swing is a complete follow-through swing that is typically used during a standard batting attempt. In contrast, a check swing occurs when the batter starts to swing but stops the motion midway, often in response to a last-moment decision regarding the pitch. These two swing types were selected to analyze how different dynamic movements affect the mechanical forces on the hamate under varied grip conditions.
This comprehensive examination of grip and swing types aimed to illuminate the biomechanical interactions that contribute to hamate stress, providing crucial insights that could help in refining batting techniques to prevent injuries and enhance player performance.
Findings on Pressure and Wrist Kinematics: Hitting Grip and Hand Position
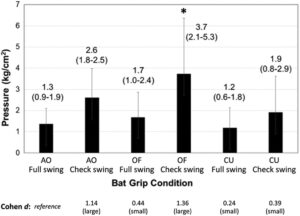 The study's findings revealed significant insights into how different batting techniques affect the biomechanical stresses placed on the wrist, specifically focusing on the hamate bone. Among the grip variations analyzed, the One Off (OF) check swing condition was notably impactful, showing the highest pressures on the hamate. This particular result is critical as it underscores a potential increase in the risk of fractures. The OF grip, with the pinky finger of the bat knob, may cause the remaining fingers to redistribute and possibly intensify pressure onto the hamate bone during the abrupt stopping motion of a check swing.
The study's findings revealed significant insights into how different batting techniques affect the biomechanical stresses placed on the wrist, specifically focusing on the hamate bone. Among the grip variations analyzed, the One Off (OF) check swing condition was notably impactful, showing the highest pressures on the hamate. This particular result is critical as it underscores a potential increase in the risk of fractures. The OF grip, with the pinky finger of the bat knob, may cause the remaining fingers to redistribute and possibly intensify pressure onto the hamate bone during the abrupt stopping motion of a check swing.
Furthermore, the study highlighted distinct differences in wrist kinematics between check swings and full swings. Check swings typically resulted in lower wrist velocities, which can be attributed to the shorter and more controlled motion range compared to the more dynamic and extensive movement of a full swing. This reduced velocity suggests that the wrist is undergoing different stress patterns during check swings, which might contribute to how pressures are focused and exerted on the hamate bone.
Additionally, the wrist motion dynamics observed during check swings were different from those seen in full swings. Check swings involve a rapid deceleration as the player stops the bat mid-swing, which can lead to a sudden increase in loading on specific areas of the wrist, such as the hamate bone. This contrasts with full swings, where the motion is more fluid and continuous, allowing for a more even distribution of forces across the wrist.
These findings are crucial for understanding the mechanical stressors involved in different batting techniques and their implications for injury risk. By identifying the conditions under which the hamate is subjected to the highest pressures, coaches and players can adjust training and technique to mitigate these risks, potentially reducing the incidence of hamate fractures and enhancing overall player safety and performance.
Implications for Practice: Hitting Grip and Hand Position
 The findings from this study carry important implications for baseball practice and player safety. The identification of specific bat grips, particularly the One Off (OF) condition combined with check swings, as potential risk factors for hamate injuries, signals a need for careful consideration of batting techniques during training and gameplay.
The findings from this study carry important implications for baseball practice and player safety. The identification of specific bat grips, particularly the One Off (OF) condition combined with check swings, as potential risk factors for hamate injuries, signals a need for careful consideration of batting techniques during training and gameplay.
Adjusting Grip Techniques: Coaches and players may need to revisit the grip techniques currently being taught and utilized. Training sessions could incorporate drills that not only focus on improving performance but also on optimizing grip positions to reduce undue stress on the hamate bone. Players, especially those recovering from previous wrist injuries or those particularly vulnerable, might benefit from tailored grip adjustments that consider individual anatomical and performance needs.
Modifications to Bat Design: The study's insights also open up possibilities for bat design modifications. Manufacturers might explore designs that alter the shape of the bat knob to distribute pressure more evenly across the hand, thus minimizing peak stress points on the hamate bone. This could include bats with ergonomically shaped knobs or additional padding where the hand meets the bat knob.
Educational Programs: Implementing educational programs for players on the risks associated with different types of swings and grips can further aid in injury prevention. By educating players about the mechanics of injury and how modifications in their swinging technique can decrease risks, players can make more informed choices about their at-bat strategies.
Further Research: Additionally, the results suggest the need for further research into other grip styles and their biomechanical impacts. Such studies could lead to a deeper understanding of how various aspects of batting influence the risk of hamate injuries and other common sports-related injuries.
Monitoring and Feedback Systems: Integrating technology such as pressure sensors in gloves or on bats during practice could provide real-time feedback to players and coaches about grip and swing impact. This technology can be used to monitor stresses on the hamate and adjust techniques immediately, potentially preventing injury before it occurs.
By addressing these implications, the baseball community can enhance player welfare, extend athletic careers, and potentially improve game performance through healthier, more scientifically informed approaches to batting.
Explore Optimal Swing Mechanics with the GFT Hitting Program
 Unlock your full potential at the plate with the GFT Hitting Program, exclusively available at TopVelocity.net/GFT. Designed to refine and perfect your hitting skills, this program utilizes the latest in sports science to help you master the art of batting.
Unlock your full potential at the plate with the GFT Hitting Program, exclusively available at TopVelocity.net/GFT. Designed to refine and perfect your hitting skills, this program utilizes the latest in sports science to help you master the art of batting.
Why Choose the GFT Hitting Program?
In baseball, every swing counts. Developing the right hitting mechanics is crucial not only for performance but also for longevity in the sport. The GFT Hitting Program is tailored to help athletes of all levels enhance their swing mechanics through a comprehensive approach that combines biomechanics, professional coaching, and advanced technology.
Key Benefits of the Program:
- Biomechanical Analysis: Learn about the intricate details of your swing mechanics. The program uses high-speed video analysis to break down your swing and identify areas for improvement.
- Personalized Coaching: Receive personalized feedback from experienced coaches who understand the nuances of hitting at both amateur and professional levels. Our coaches help you adjust your technique in real-time.
- Strength and Conditioning: Beyond just technique, the program includes targeted strength and conditioning exercises that enhance the physical attributes needed for a powerful swing, such as rotational strength, wrist stability, and core power.
- Mental Training: Hitting is as much mental as it is physical. Our program addresses the psychological aspects of batting, helping you develop the confidence and focus necessary to succeed in high-pressure situations.
Develop Your Swing Mechanics:
Whether you're starting out or looking to play at higher levels, the GFT Hitting Program provides the tools you need to succeed. By focusing on the fundamentals and advanced aspects of hitting, you'll learn how to optimize your swing for both power and consistency.
Join Now:
Don’t miss the opportunity to transform your game. Visit TopVelocity.net/GFT today to learn more about the GFT Hitting Program and start your journey to becoming a better hitter. Take the first step towards unlocking your hitting potential!
Conclusion
This research highlights the importance of understanding the biomechanical implications of bat grips and swing types. By tailoring equipment and training techniques, it may be possible to reduce the incidence of hamate fractures among baseball players, enhancing both athlete safety and performance.
FAQs
- What is a hook of hamate fracture?
- It's a type of fracture in the small hook-like bone (hamate) in the wrist, often caused by sports that involve gripping equipment.
- How can changing bat grips reduce injury risk?
- Altering how the bat is held can redistribute the pressures exerted during a swing, potentially decreasing stress on vulnerable areas like the hamate.
- What were the key findings of the study?
- The study found that certain grips combined with check swings could significantly increase pressure on the hamate, thus raising injury risks.
- How does this study impact baseball training?
- The insights can guide coaches and players in choosing safer grip techniques and customizing training to prevent common injuries.
- Can bat modifications help in reducing hamate stress?
- Yes, using bats designed to reduce knob impingement on the hamate can help lower the pressures during batting.




