The Stretch-Shortening Cycle (SSC) is a fundamental biomechanical concept that is pivotal across various sports, particularly in activities requiring explosive movements. SSC is characterized by three distinct phases: an eccentric phase where the muscle lengthens, an amortization phase which is a brief transitional pause, and a concentric phase where the muscle shortens rapidly. This cycle exploits the elastic properties of muscles and connective tissues, allowing for a significant release of stored elastic energy. In the context of pitching, the SSC is initiated when a pitcher starts their wind-up, stretches their muscles during the stride, and finally explosively contracts these muscles to deliver the pitch.
In baseball pitching, mastering the SSC is crucial for performance enhancement and injury prevention. Effective utilization of the SSC can markedly increase the velocity of the pitch. During a pitch, the pitcher’s body acts as a coordinated chain, with energy flowing from the legs and hips, through the torso, and finally to the arm. Each segment of this kinetic chain must be timed perfectly to maximize the energy transfer and to make full use of the SSC. Not only does this result in more powerful pitches, but it also distributes the physical stress more evenly across the body, which can reduce the risk of localized injuries. Thus, understanding and optimizing the SSC is not just about improving performance—it's also about fostering longevity in a pitcher's career by mitigating the wear and tear that high-velocity pitching can inflict on the body.
The Basics of the Stretch Shortening Cycle
 Definition and Components of Stretch Shortening Cycle
Definition and Components of Stretch Shortening Cycle
The Stretch-Shortening Cycle (SSC) is a dynamic and complex process that enhances muscular performance by utilizing the natural elastic properties of muscle and tendon structures. It consists of three main components:
- Eccentric Phase: This initial phase involves the pre-stretching of the muscle group that is about to be used. In pitching, this would be the action as the pitcher winds up and the muscles of the arm, shoulder, and trunk are lengthened under tension.
- Amortization Phase: Following the stretch, there is a brief transitional period where the muscle remains in a semi-contracted state. This phase is critical and must be as short as possible to maximize the potential energy stored during the eccentric phase. The shorter this phase, the more effective the subsequent muscle contraction will be.
- Concentric Phase: This is the explosive phase of the cycle where the pre-stretched muscles contract powerfully to perform the desired action. For a pitcher, this phase corresponds to the rapid forward motion of the arm to release the ball at high speeds.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the mechanics of movement, and the efficiency of transitioning between these phases determines the effectiveness of the SSC.
Biomechanical Insights: How Stretch Shortening Cycle Works
Biomechanically, the SSC operates on the principle of energy efficiency and conservation. When a muscle elongates during the eccentric phase, it stores potential elastic energy in the tendons and muscle fibers. If the transition to the concentric phase is quick (optimized amortization phase), this stored energy is released along with the muscular force, significantly increasing the total power output.
This mechanism is akin to a rubber band being stretched and then released; the more it stretches, the more energy it releases. In biomechanical terms, this process involves complex interactions between neural signals and mechanical muscle properties. Muscles are pre-activated before they stretch, setting the stage for a powerful recoil. Additionally, the sensory receptors within the muscles, such as the muscle spindles, provide feedback to the central nervous system to regulate muscle stiffness and timing of contraction, ensuring that the concentric phase is as potent as possible.
The effective use of SSC can drastically enhance performance in sports like baseball, where the difference in milliseconds in muscle response times can significantly influence the speed and control of a pitch. Moreover, understanding and training these biomechanical interactions can help athletes not only improve their performance but also reduce the risk of injury by promoting more efficient movement patterns. This understanding is crucial for trainers and coaches who aim to develop athlete-specific conditioning programs that enhance the natural biomechanical advantages provided by the SSC.
Hip to Shoulder Separation and Its Role in Stretch Shortening Cycle
 Understanding Hip Shoulder Separation
Understanding Hip Shoulder Separation
Hip shoulder separation is a key biomechanical concept in pitching mechanics, referring to the angular difference between the orientation of the hips and the shoulders. This separation occurs when a pitcher's hips begin to rotate towards the plate while the shoulders remain closed or aligned towards third base for a right-handed pitcher (or first base for a left-handed pitcher). This creates a torsional stretch across the pitcher's trunk, particularly affecting the muscles of the core and the lower back.
This mechanism is crucial because it sets the stage for a powerful release of energy. The greater the separation between the hips and shoulders, the more potential energy is stored within the torso's musculature, much like winding up a spring. This stored energy, when released, helps accelerate the upper body and arm towards the plate, contributing to a faster and more powerful pitch.
The Impact of Hip Shoulder Separation on Pitch Velocity
The role of hip shoulder separation in enhancing pitch velocity is substantial due to its direct impact on the dynamics of the stretch-shortening cycle. When a pitcher achieves maximum hip shoulder separation, they effectively utilize the SSC to convert the stored elastic energy into kinetic energy.
- Increased Elastic Energy: As the hips rotate to face the home plate, the shoulders and the arm continue to move back or stay loaded, increasing the stretch on the oblique muscles and the connective tissues across the shoulder girdle. This action stores a considerable amount of elastic energy, much like stretching an elastic band to its limit.
- Enhanced Force Production: The rapid uncoiling of the body—first the hips, then the torso, followed by the arm—translates this elastic energy into a powerful movement. The speed at which this uncoiling happens can significantly amplify the force generated, much like releasing a tightly wound spring. This explosive action contributes directly to the speed of the pitch, as the energy flows from the core of the body through the arm and into the ball.
- Optimized Timing: The effectiveness of hip shoulder separation also depends on the timing of the rotation. If the shoulders begin to rotate too soon, it diminishes the stretch and potential energy that can be accumulated. Conversely, if the timing is perfectly synced, the release of energy is maximized, enhancing pitch velocity.
The biomechanical advantage provided by optimal hip shoulder separation is critical for pitchers seeking to maximize their performance. It not only contributes to the velocity but also to the overall efficiency of the pitching motion, reducing the stress on the arm by distributing forces more evenly throughout the body. This is why pitchers and coaches focus intensely on drills and techniques that enhance and perfect the separation and timing of hip and shoulder movements, integral elements in the development of elite pitching performance.
Kinematics of Pitching: An Overview
 The Relationship Between Trunk Rotation and Pitch Velocity
The Relationship Between Trunk Rotation and Pitch Velocity
Trunk rotation plays a pivotal role in the pitching process, serving as the central mechanism through which force is transferred from the lower body to the upper body and ultimately to the baseball. The kinetic chain in a pitch starts from the ground up, with force generation beginning in the legs and hips, which is then amplified through the trunk and transferred through the arm to the ball.
The speed and efficiency of trunk rotation are critical in determining pitch velocity. A swift and smooth trunk rotation can significantly increase the momentum of the pitching arm, leading to faster pitches. This rotation involves a complex coordination of muscle groups, including the abdominals, lower back, obliques, and the spinal erectors. These muscle groups work together to rotate the torso, culminating in the rapid forward motion required for a high-velocity pitch.
Biomechanical studies have shown that the degree of trunk rotation and the speed at which it occurs are directly correlated with the pitch speed. Pitchers with greater trunk rotational velocities can impart more kinetic energy to the ball. This relationship underscores the importance of core strength and flexibility in pitchers, as these physical traits enhance the ability to rotate quickly and with greater force.
Kinematic Sequencing in Pitching
Kinematic sequencing refers to the order and timing of movement across different body segments during a pitch. This sequence is crucial for maximizing efficiency and power during the pitching motion. Proper kinematic sequencing ensures that each segment of the body contributes optimally to the final action—the release of the baseball.
The typical sequence in an effective pitch begins with the lower body, particularly the legs and hips, initiating the movement. As the pitcher steps toward the plate, the hips begin to rotate toward the target, creating the initial force and momentum necessary for the pitch. Following the hip rotation, the trunk begins to rotate, adding to the velocity generated by the lower body.
Finally, the sequence culminates in the arm action. As the trunk completes its rotation, the shoulder and arm whip forward, using the built-up energy from the lower body and trunk. This final transfer of energy is crucial and needs to be precisely timed. If the arm lags too far behind, or if it moves too early, it can disrupt the flow of energy and reduce the effectiveness and speed of the pitch.
The success of kinematic sequencing is highly dependent on the pitcher’s ability to coordinate these movements fluidly and efficiently. Training in kinematic sequencing focuses on enhancing this coordination, often through drills that isolate and then integrate each part of the kinetic chain. This training not only improves pitch velocity and control but also helps in reducing the risk of injury by ensuring that no single part of the body is overstressed during the pitching process.
Understanding and optimizing the kinematics of pitching are central to a pitcher's success and longevity in the sport. By mastering the intricacies of trunk rotation and kinematic sequencing, pitchers can enhance their performance significantly, achieving greater pitch velocities with more consistency and less physical strain.
Pelvic and Oblique Musculature in Stretch Shortening Cycle
 The Role of the Pelvis in Pitching Mechanics
The Role of the Pelvis in Pitching Mechanics
The pelvis serves as a foundational element in the biomechanics of pitching, acting as the critical link between the lower and upper body movements. Its role in pitching mechanics is multifaceted, contributing to both stability and mobility which are essential for an effective pitching motion.
- Stability and Support: The pelvis provides a stable base from which the legs and torso can generate and transfer force. During the pitching motion, the stability of the pelvis ensures that the energy generated by the lower body is efficiently transferred through the trunk and into the arm. Any instability in the pelvic region can lead to a significant loss of power and effectiveness in the pitch, and potentially increase the risk of injury.
- Mobility for Force Transfer: While stability is crucial, the mobility of the pelvis is equally important. The pelvis needs to rotate effectively to allow for maximum hip-shoulder separation, which is key to achieving high pitching velocities. This rotation helps to stretch the muscles of the trunk, particularly the obliques, which then forcefully contract to drive the pitching motion.
- Coordination and Timing: The movement of the pelvis must be precisely coordinated with the actions of the legs, trunk, and arm to optimize the pitching sequence. The timing of pelvic rotation often sets the rhythm for the entire pitching motion, influencing the kinetic chain from the ground up.
How Oblique Musculature Influences Pitching
The oblique muscles play a vital role in the mechanics of pitching, primarily through their involvement in trunk rotation and bending motions. These muscles are crucial for the stretch-shortening cycle (SSC) that occurs during a pitch.
- Energy Storage and Release: During the wind-up and early pitching phases, the oblique muscles on one side of the body are elongated as the pitcher rotates the trunk away from the throwing arm. This stretching stores elastic energy within the muscle fibers. When the pitch is executed, these pre-stretched oblique muscles contract rapidly, releasing stored energy in a powerful rotation that contributes to the arm's velocity.
- Enhancing Hip-Shoulder Separation: The obliques are directly involved in creating and controlling the degree of hip-shoulder separation—a key factor in pitch velocity. Effective use of the obliques can increase this separation, allowing pitchers to store more elastic energy and generate greater force during the pitch.
- Stabilization and Injury Prevention: Beyond their dynamic role in force production, the oblique muscles also help stabilize the spine and trunk during the rapid, high-intensity motions of pitching. This stabilization is crucial for maintaining proper pitching mechanics and preventing injuries, particularly to the lower back and shoulders.
- Adaptation and Strength Training: Pitchers often focus on strengthening their oblique muscles through targeted exercises, such as Russian twists, side planks, and medicine ball throws. These exercises enhance the strength and responsiveness of the obliques, improving their ability to perform during pitching.
Understanding and optimizing the function of the pelvic and oblique musculature is essential for pitchers aiming to enhance their performance. The interplay between pelvic stability, oblique strength, and coordinated movement defines the efficiency of the pitching motion and influences the overall effectiveness and safety of the pitcher's technique.
The Role of Trunk Rotation in Stretch Shortening Cycle
 Maximizing Trunk Rotation for Optimal Performance
Maximizing Trunk Rotation for Optimal Performance
Trunk rotation is a crucial element in the stretch-shortening cycle (SSC) for pitching, acting as the bridge that transfers the energy generated from the lower body to the pitching arm. The effectiveness of this transfer greatly impacts the pitcher's performance, specifically the speed and power of the throw. To maximize trunk rotation for optimal performance, pitchers must focus on several key aspects:
- Core Strength and Stability: A strong and stable core is essential for effective trunk rotation. The core muscles, including the abdominals, obliques, and lower back, provide the necessary support to control and maximize the rotational movement. Strengthening these muscles through targeted exercises can enhance a pitcher's ability to rotate swiftly and with greater force.
- Flexibility and Range of Motion: Flexibility in the trunk and spine allows for a larger range of motion during rotation, which can lead to a more powerful pitch. Incorporating flexibility training and dynamic stretching into a routine helps increase the trunk's rotational capacity, enabling a more complete and forceful rotation.
- Proper Technique: The technique of trunk rotation involves not just the rotation itself but also the timing and coordination with other body parts. Proper alignment and sequencing during the pitching motion ensure that the trunk rotates at the optimal time to maximize energy transfer and minimize the risk of injury.
- Balanced Training: Focusing on both sides of the body is crucial, even though one side may be more dominant in the pitching process. Balanced muscular development prevents imbalances and enhances overall trunk rotation capability, contributing to better performance and injury prevention.
Techniques to Increase Trunk Rotation Velocity
Increasing the velocity of trunk rotation can significantly enhance pitch speed. This requires not only physical conditioning but also technical adjustments:
- Explosive Core Training: Incorporating plyometric exercises that stimulate the core muscles in an explosive manner can enhance the speed of trunk rotation. Exercises such as medicine ball throws and rotational sprints activate and strengthen the muscles involved in fast, powerful twists.
- Motor Control Improvements: Enhancing motor control through drills and practice allows pitchers to refine their trunk rotation technique. Drills that focus on the timing and sharpness of the rotation help in fine-tuning the movement to achieve higher speeds.
- Technological Assistance: Modern technology such as high-speed cameras and motion analysis software can provide pitchers with immediate feedback on their trunk rotation mechanics. This data helps in making precise adjustments to improve rotation speed.
- Specific Conditioning: Tailored conditioning programs that focus on the muscles and movements involved in trunk rotation can increase muscular responsiveness and speed. This might include rotational cable workouts, band-resisted rotation exercises, and specific strength training routines that focus on the rapid activation of core muscles.
By enhancing trunk rotation through these techniques, pitchers can tap into the full potential of the SSC, thereby boosting their pitching performance through more effective and efficient energy transfer from the lower body through the trunk to the arm. Each of these techniques contributes to the overall capability to deliver faster, more powerful pitches consistently and with less risk of injury.
Stretch Shortening Cycle's Influence on Shoulder Kinematics
 Shoulder External Rotation and Pitching Velocity
Shoulder External Rotation and Pitching Velocity
Shoulder external rotation plays a critical role in the mechanics of pitching, particularly in how it influences pitch velocity through the stretch-shortening cycle (SSC). This rotation is part of the pitching arm action where the arm moves backward, effectively winding up before rapidly moving forward to release the ball. The dynamics of external rotation are closely tied to the SSC because they involve the pre-stretching of the internal rotator muscles of the shoulder.
- Elastic Energy Storage: As the pitcher's arm winds up and the shoulder externally rotates, the internal rotators of the shoulder are stretched, storing elastic energy in a similar manner to a spring being compressed. This stored energy is crucial for the subsequent phase of the pitch.
- Rapid Energy Release: Following the wind-up, the stored energy is released as the shoulder transitions into internal rotation. This rapid release contributes significantly to the acceleration of the arm, thus increasing the velocity of the pitch. The more intense the external rotation and the quicker the transition to internal rotation, the more energy can be transferred to the ball.
- Enhancing Performance: Optimizing shoulder external rotation can lead to significant improvements in pitch velocity. This involves not only strengthening the muscles involved but also increasing their flexibility and the overall range of motion of the shoulder joint.
The Interaction Between Trunk and Shoulder Movement
The synchronization of trunk and shoulder movements is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of the stretch-shortening cycle in pitching. These two components of the pitching motion are deeply interconnected, with each influencing the efficiency and power of the other.
- Sequential Kinetic Chain Activation: In an effective pitch, the trunk begins to rotate towards the plate once the pitcher's lead foot hits the ground. This trunk rotation helps to stretch the muscles around the shoulder, priming them for explosive action. As the trunk reaches its maximum rotation, the shoulder then follows, with external rotation culminating in a powerful internal rotation as the ball is released.
- Energy Transfer Efficiency: The timing between trunk rotation and shoulder movement is crucial. If the trunk rotates too early or too late relative to the shoulder movement, it can disrupt the flow of kinetic energy along the kinetic chain, reducing the overall force and speed of the pitch. Proper coordination ensures that the energy generated from the lower body and trunk is effectively transferred through the shoulder to the arm and ultimately to the ball.
- Training for Coordination: To enhance this interaction, pitchers often engage in drills that focus on the timing and fluidity of trunk and shoulder rotations. These drills help to refine the motor skills needed to synchronize these movements, ensuring that the maximum amount of kinetic energy is conserved and utilized during the pitch.
The influence of the SSC on shoulder kinematics is a cornerstone of high-velocity pitching. By understanding and optimizing the external rotation of the shoulder and its coordination with trunk movement, pitchers can significantly enhance their performance, increasing both the speed and control of their pitches.
3X Velocity Development Kit with the Trunk Excelerator
 Unlock the true potential of your pitching and throwing abilities with the revolutionary 3X Velocity Development Kit featuring the Trunk Excelerator by TopVelocity. This cutting-edge training solution is engineered to redefine how players approach velocity development, focusing on harnessing the power of the trunk to propel performance to unprecedented levels.
Unlock the true potential of your pitching and throwing abilities with the revolutionary 3X Velocity Development Kit featuring the Trunk Excelerator by TopVelocity. This cutting-edge training solution is engineered to redefine how players approach velocity development, focusing on harnessing the power of the trunk to propel performance to unprecedented levels.
Key Features of the 3X Velocity Development Kit with Trunk Excelerator:
- Advanced Training Innovation: The Trunk Excelerator is a breakthrough device that revolutionizes velocity development by refining trunk mechanics, redistributing energy, and optimizing power transfer. By immobilizing the arms and placing emphasis on trunk engagement, this device maximizes the efficiency of every movement, leading to significant gains in performance.
- Focused Trunk Development: With the arms locked in position and the trunk at the forefront of movement, athletes experience targeted trunk development like never before. By isolating and enhancing trunk power, the 3X Velocity Development Kit facilitates a stronger, more explosive delivery, resulting in enhanced velocity and precision on the field.
- Immediate Performance Enhancement: Upon donning the device, athletes may initially experience a decrease in velocity and arm stress. However, this temporary setback is a catalyst for rapid trunk improvement. As athletes adapt to the device and refine their trunk mechanics, they will witness a remarkable surge in throwing velocity, often achieving personal records immediately upon its removal.
- Evidence-Based Design: The efficacy of the Trunk Excelerator is substantiated by a comprehensive case study conducted by Aguinaldo and Escamilla (2019). This study highlights the pivotal role of trunk motion in generating power and velocity during pitching, with approximately 86% of energy transfer originating from trunk movement. By aligning with these findings, the 3X Velocity Development Kit empowers athletes to capitalize on the biomechanical principles that drive elite performance.
- Comprehensive Training Package: In addition to the Trunk Excelerator, the 3X Velocity Development Kit includes a comprehensive training program complete with drills, exercises, and instructional materials. Athletes gain access to expert guidance and resources designed to optimize their training regimen and accelerate their progress toward peak performance.
Elevate Your Game
Whether you're a pitcher seeking to dominate the mound or a position player looking to enhance your throwing prowess, the 3X Velocity Development Kit with Trunk Excelerator equips you with the tools and techniques to elevate your game to new heights. Gain a competitive edge, impress coaches and scouts, and unleash your full potential on the diamond.
Don't miss out on the opportunity to revolutionize your baseball performance. Order the 3X Velocity Development Kit with Trunk Excelerator today and embark on your journey towards elite velocity and unparalleled success in the sport.
For more exclusive content, visit TopVelocity Patreon!


 Understanding Hip Shoulder Separation
Understanding Hip Shoulder Separation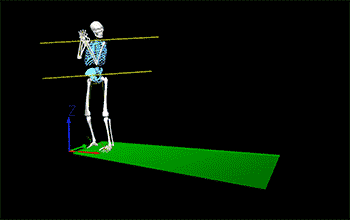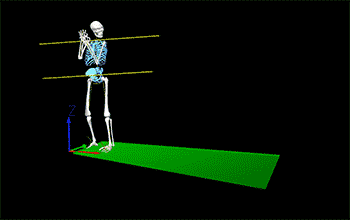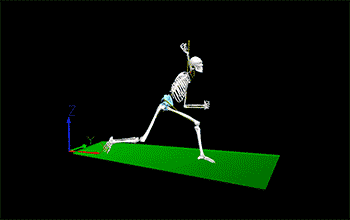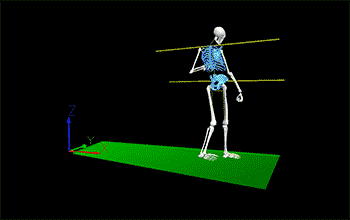 The Relationship Between Trunk Rotation and Pitch Velocity
The Relationship Between Trunk Rotation and Pitch Velocity The Role of the Pelvis in Pitching Mechanics
The Role of the Pelvis in Pitching Mechanics Maximizing Trunk Rotation for Optimal Performance
Maximizing Trunk Rotation for Optimal Performance Shoulder External Rotation and Pitching Velocity
Shoulder External Rotation and Pitching Velocity

